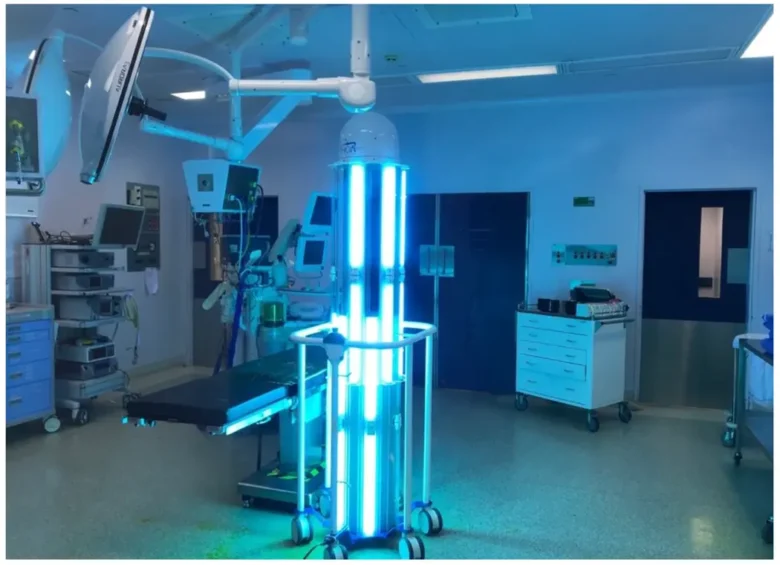
Advanced UV sterilization technology is revolutionizing infection prevention in hospitals worldwide. This innovative approach improves sterility and protects patients and healthcare workers from germs. UV sterilization is a chemical-free alternative to standard cleaning methods and a powerful weapon in the fight against hospital-acquired infections. Hospitals strive to reduce infection rates while maintaining efficiency.
UV technology is a scientifically proven method for killing bacteria, viruses, and other germs. UV sterilization systems usher in a new era of hospital hygiene, combining technology with medical care to improve patient safety. This new approach to infection control solves existing problems and prepares hospitals for future health risks. Understanding how UV sterilization works and its application in hospitals can reveal its importance to modern healthcare.
The Rising Challenge of Hospital Infections:
Healthcare facilities worldwide are facing the problem of hospital-acquired infections, which threaten patient safety and the effectiveness of treatment. Hospital-acquired infections affect millions of patients annually, prolonging hospital stays, increasing healthcare costs, and leading to deaths. Traditional cleaning methods can eliminate some, but not all, pathogenic microorganisms in complex healthcare environments. Antibiotic-resistant microorganisms are resistant to conventional treatments, further complicating the problem.
Healthcare institutions must balance sterility and efficiency without compromising patient care. In addition to the cost of treatment, hospital-acquired infections also incur liability, compliance, and reputation management costs. Modern hospitals must control airborne infections and hard-to-reach contamination beyond surface cleaning. Healthcare leaders are seeking innovative sterilization methods that do not use toxic chemicals to meet this growing demand.
Understanding UV Sterilization Technology:
UV sterilization uses UV-C radiation with a wavelength of 200-280 nanometers to kill dangerous bacteria. This method destroys the DNA and RNA of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other pathogens, preventing bacterial growth and infection. UV sterilization uses a photochemical process to generate thymine dimers, which inhibit the proper functioning of bacteria.
In healthcare, UV-C is the most effective wavelength for UV sterilization. Direct exposure to UV light can sterilize a target surface or airspace. UV sterilization systems can be fixed, portable, or integrated into hospital ventilation systems. The effectiveness of UV sterilization depends on exposure time, light intensity, distance from the UV source, and shadows or obstacles that block light penetration. Understanding these technical aspects can help hospitals improve their UV sterilization processes and control infections.
UV Sterilization Applications in Hospitals:
Hospitals offer a variety of UV sterilization options for different departments and operating rooms. UV sterilization systems can improve operating room conditions by disinfecting surgical instruments, surfaces, and air circulation systems in the operating room. After patients are discharged, portable UV units are used to clean patient rooms to eliminate pathogens before new patients are admitted. UV sterilization can quickly disinfect high-traffic emergency departments where conventional cleaning procedures may not meet the cleaning requirements.
Laboratory facilities use UV technology to maintain sterility in critical testing areas and sample storage areas. UV sterilization can protect critically ill patients susceptible to infections in intensive care units. UV systems maintain sterility in drug preparation and distribution facilities. UV sterilization in hospital ventilation systems reduces the presence of airborne pathogens. Storage areas for medical supplies and equipment benefit from UV treatment to prevent contamination. These applications demonstrate how UV technology can solve infection control problems in various medical departments and surgeries.
Benefits of UV Sterilization in Hospitals:
UV sterilization technology improves infection control in hospitals and increases efficiency. Chemical-free disinfection minimizes patient and staff concerns about harmful residues and chemical sensitivities. Rapid sterilization cycles increase hospital productivity and patient capacity by speeding up the turnaround of patient rooms and equipment processing. Standard cleaning procedures cannot remove bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores, but broad-spectrum antimicrobials do.
UV systems are cost-effective because they reduce the use of chemical disinfectants and infection costs. Environmental sustainability benefits include less chemical waste and a lower environmental impact than traditional disinfection methods. Sterilization protocols can be automated, reducing procedural errors. Documentation and monitoring features record sterilization cycles to ensure compliance and quality assurance. Reduced exposure to chemical disinfectants and automated sterilization improves staff safety. These benefits improve patient outcomes, lower healthcare costs, and increase hospital efficiency.
Challenges and Considerations:
Despite its success, UV sterilization technology has also presented some obstacles and challenges that hospitals face during implementation and operation. Without adequate protection, UV-C radiation can damage the skin and eyes, so safety measures must be carefully planned. Due to the high initial cost of UV sterilization systems, careful budgeting and a return on investment (ROI) analysis are required. To achieve consistent sterilization results, light source replacement, system calibration, and performance monitoring are necessary.
Objects that block UV light can create shadows where infections can grow, so precise settings and multiple lighting angles are required. Hospital staff must be trained in the operation, safety, and troubleshooting of UV sterilization systems. There are also some challenges in integrating UV technology into hospital infrastructure and workflows. To meet regulatory requirements, UV sterilization equipment must be approved and meet medical institutions. Implementing quality assurance technology is crucial to monitor sterilization results and demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements. UV sterilization in hospitals requires careful planning, staff training, and ongoing maintenance.
Future Trends in UV Sterilization:
Innovative UV sterilization technology is expected to improve sterilization efficiency and expand its use in healthcare. Smart UV systems use artificial intelligence (AI) to optimize sterilization based on environmental variables and contaminants. LED UV systems have a longer lifespan, lower energy consumption, and more efficient wavelength management than mercury lamps. Portable and wearable UV devices provide safety for healthcare workers in high-risk areas.
Advanced monitoring systems utilize real-time sensors and data analytics to maintain sterility and detect malfunctions early. UV sterilization and other disinfection processes can be used to build infection control systems. Robotic systems can sterilize large hospital spaces with UV without human intervention. Safe and germicidal wavelengths are central to the development of Far-UVC technology. These trends suggest that UV sterilization will become more efficient, user-friendly, and better integrated into infection control measures in hospitals.
Conclusion:
UV sterilization technology has revolutionized infection management in hospitals, enabling them to combat pathogens while simultaneously improving efficiency. UV systems for hospitals reflect the healthcare sector’s investment in new solutions for patient and staff safety. As technology advances, UV sterilization becomes more advanced, easier to use, and more effective in addressing emerging health challenges.
UV sterilization technology places healthcare institutions at the forefront of infection control innovation and potentially saves operating costs. Comprehensive planning, training, safety procedures, and system maintenance are crucial to the success of UV sterilization. UV technology improves effectiveness and increases utilization, making this investment more attractive to healthcare institutions. UV sterilization technology has revolutionized infection management in hospitals, making care safer and more efficient for patients and staff.
FAQs:
1. Is UV sterilization safe for patients and staff?
UV-C sterilization is safe when safety standards are followed, such as avoiding human exposure and wearing protective clothing.
2. When does UV sterilization work?
UV sterilization typically takes a few minutes to 30 minutes to disinfect a space, depending on the technology and the microorganisms.
3. Can UV sterilization replace traditional cleaning methods?
UV sterilization works best on clean surfaces and requires direct visibility, so it complements cleaning, not replaces it.
4. What pathogens does UV sterilization kill?
UV-C disinfection kills bacteria, viruses, fungi, spores, and antibiotic-resistant strains, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Clostridium difficile.
5. How much does a UV disinfection system cost in a hospital?
UV disinfection systems can range in price from a few thousand to tens of thousands of euros, depending on the system type and capacity.