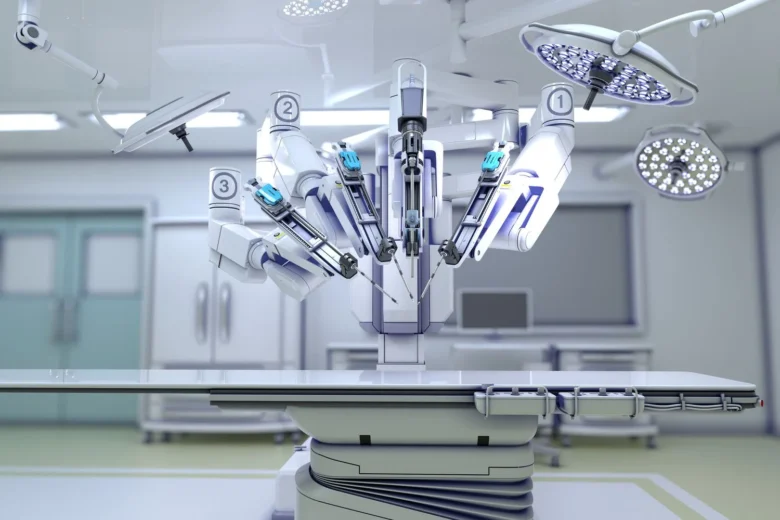
Robotic surgery is one of the most groundbreaking and fascinating developments in modern medicine. Robots help surgeons perform complex surgeries with much greater accuracy, flexibility, and control than traditional surgery. Over the past few decades, robot-assisted surgery has become increasingly common in a wide range of medical fields, including urology, gynecology, orthopedics, and cardiothoracic surgery. In a short period, these technologies have advanced significantly, and recent advancements are expanding the capabilities of operating rooms globally.
Development of Robotic Surgical Systems
The Da Vinci Surgical System is one of the most widely used robotic surgical systems today. The system was originally produced in the 1980s and 1990s. These systems typically feature robotic arms that the surgeon controls through a console that displays a high-resolution 3D image of the surgical site. The robotic instruments move more delicately and precisely based on the surgeon’s movements. This makes it possible to minimize surgical trauma, reducing the risk of infection, blood loss, and recovery time. Recent research focuses on improving these systems to make them more precise, adaptable, and better designed.
Better Control and Precision
One of the latest advances in robotic surgery is improved precision and control. Surgeons can now sense pressure and resistance with robotic instruments thanks to new systems that use enhanced tactile feedback. This extra sense of touch is extremely useful for delicate surgeries, such as nerve-sparing surgeries, where precision is key. New instruments move and function in a way that mimics the support of a human hand and eliminates natural vibrations. These improvements make surgeries on the brain, spine, and even delicate eye tissue more precise and reliable.
Shrinking Robotic Devices
The miniaturization of robotic surgical instruments is another major advancement. Researchers and engineers are creating robots that are small enough to enter the body through natural openings or small incisions. These microrobots can move in tight spaces, perform complex tasks, and even be assembled inside the body. Some surgical robots are sthey can be eaten, and theyt in a pill, can be eaten, and can be controlled remotely to perform biopsies or inject targeted medications. This technology enables minimally invasive surgery, which means less trauma and faster healing.
AI in Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery is increasingly using AI. AI systems can analyze large amounts of data from previous surgeries to support planning and decision-making. AI can support surgeons during surgeries by pinpointing important anatomical landmarks, alerting them to potential errors, and suggesting optimal surgical options. Machine learning algorithms improve with each surgery, making subsequent surgeries more efficient. These smart devices provide surgeons with real-time data analysis, allowing them to perform more complex surgeries with better results and fewer problems.
Remote surgery and Telesurgery Opportunities
Remote surgery, or telesurgery, is one of the most innovative applications of robotic surgery. It means that surgeons can control a robotic system from a location far away from the patient. With high-speed internet and real-time communication, surgeons in one country can operate on a patient in another. Remote robotic surgery is still in its infancy due to latency and connectivity issues, but successful demonstrations have shown that this approach is feasible. This technology could enable patients in remote or underserved areas to receive specialized treatment and change the way care is delivered worldwide.
Applications in Cancer Tenormousent
Robotic surgery has great potential in cancer treatment. Robotics can improve physician control and accuracy during operations for prostate, lung, kidney, and reproductive organ cancers. Minimally invasive robotic technology allows surgeons to remove tumors with clean margins while preserving surrounding healthy tissue. Recent advancements also include the use of imaging technologies such as real-time magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or fluorescence imaging in robotic systems. This allows surgeons to see tumors more clearly during surgery. These new technologies increase the effectiveness of cancer treatments and reduce the risk of recurrence.
Enhanced Training and Simulation
Another area of advancement is the use of advanced simulation systems to guide future surgeons. Modern robotic surgery platforms feature virtual reality environments that allow surgeons in training to practice surgeries without having to perform them on real patients. These simulations are similar to real life, providing hands-on experience in a safe and controlled environment. Surgeons can receive immediate feedback, helping them work more efficiently. Some systems use augmented reality to display the anatomy of real surgeries, making them more accurate. These improvements in training are helping more surgeons use robotic equipment correctly.
Integration of Robotics and Imaging Technology
Advanced imaging technology is increasingly being integrated with modern robotic systems to make surgeries more interactive. This integration makes it possible to take pictures during surgery that show the position of organs and surgical instruments in real time. Surgeons can adjust surgical plans based on the latest developments. In neurosurgery, for example, 3D imaging can help avoid important brain structures. The combination of robotics and vision technology gives doctors greater control and clarity, improving the safety and success of surgeries.
Conclusion
Robotic surgery is revolutionizing medicine, wprocedures discoveries that make surgery safer, more precise, and more effeexpanding the limits of medical possibilities, ranging from tiny robots and AI integration to enhanceds and AI integration to better training and telework capabilities. As robotic systems become more advanced and commonplace, they offer the promise of better surgical outcomes, shorter recovery times, and access to specRobotic surgery has a promising future and will significantly influence the development ofplay a crucial role in shaping the next generation of healthcare.
FAQs
1. Is robotic surgery available everywhere?
More and more people are undergoing robotic surgery, but it may not be available in some places due to the high cost, special instruments, and training required.
2. Will robots replace surgeons?
Surgeons use robots to assist, not replace. Surgeons maintain control over the surgery and use robotic devices to improve their skills and accuracy.
3. How do doctors learn to perform robotic surgery?
To become proficient in robotic surgery, surgeons must undergo rigorous training that includes simulations, hands-on experience, and supervised procedures.
4. What does insurance cover for robotic surgery?
Robotic surgery is often covered by insurance, but the exact cost depends on the surgeon and the specific surgery.
5. What will robotic surgery look like in the future?
Smarter systems, better image integration, more powerful remote capabilities, and broader accessibility will make robotic surgery more advanced in the future.